
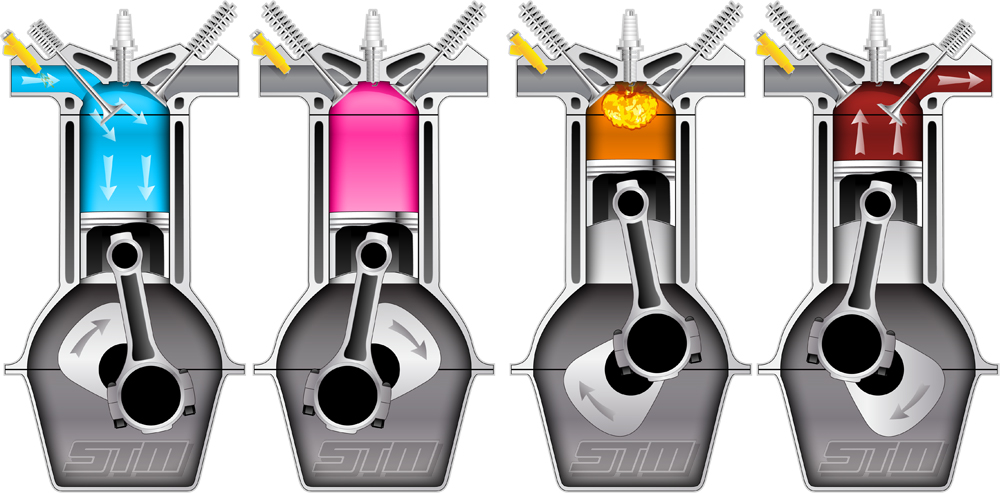
When the piston compresses the mixture up to the desired temperature and pressure, a spark plug generates a spark and ignites the mixture. The piston compresses the air-fuel mixture and increases the temperature of the mixture. In a SI engine, firstly, the carburetor mixes air and fuel then sends this mixture to the compression cylinder. This engine contains a carburetor, spark plug, fuel inject, inlet & outlet valves, reciprocating piston, connecting rod, and crankshaft. The working of the SI engine is very different than the CI engine. These engines are also known as petrol engines. Spark ignition engine is one of the most common types of IC engine. The IC engine has the following two types according to the ignition process: 1) Spark Ignition (SI) Engine The internal combustion engines have the following major types: At last, this crank movement drives the wheels of the different automobiles through a gear system. The expanding gas pushes the piston and turns the crankshaft. A piston compresses the air-fuel mixture, and a spark plug provides a spark to start the combustion of the compressed air-fuel mixture.Īfter combustion, the air-fuel mixture expands. The engine takes air from the environment and mixes it with fuel.

The IC engine contains a piston, combustion chamber, carburetor, connecting shaft, and crankshaft. Working Principle of Internal Combustion Engine

This article describes the working principle, components, and types of an internal combustion engine. In the previous article, we discussed the external combustion (EC) engine. The working and design of the IC engine are very different than the EC engine. An IC engine is a mechanical machine that burns fuel inside the engine. The internal combustion engine is a most commonly used type of engine. The engines are used all over the world for different applications. 10.4 What are the examples of internal combustion engines?.10.3 Why is it called an internal combustion engine?.10.2 What is the Purpose of Internal Combustion Engine?.9 Difference between Internal Combustion Engine and Steam Engine.8.2 Disadvantages of Internal Combustion Engines.8.1 Advantages of Internal Combustion Engines.8 Advantages and Disadvantages of IC Engine.4.6 6) According To the Design of Engine.4.5 5) Types According to Number of Strokes.4.3 3) Types According to the Cylinder Arrangement.4.2 2) Types According to the Operating Cycle.3 Working Principle of Internal Combustion Engine.2 Working of Internal Combustion Engine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
